The major psychotic disorders Medical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 4e

The beliefs that antipsychotic drugs (APDs) are 1) effective only to treat delusions and hallucinations (positive symptoms), 2) that typical and atypical APDs differ only in ability to cause extrapyramidal side effects, and 3) that their efficacy as antipsychotics is due solely to their dopamine D 2 receptor blockade are outmoded concepts that prevent clinicians from achieving optimal clinical.
How Antipsychotic Drugs Work in the Brain Video & Lesson Transcript

Buy "Memorable Psychopharmacology," "Memorable Psychiatry," and "Memorable Neurology" on Amazon! http://memorablepsych.com/books Antipsychotics are second on.
Cardiometabolic effects of psychotropic medications

Chol-promazine! (CPZ is low potency antipsychotic) Thioridazone! Getting rid of them pyramidal! (Thioridazone is low potency neuroleptic without EPS) Your moderate - molindone and loxapine! (Molindone and Loxapine are moderate potency antipsychotics) Halo, Hello high potency! (Haloperidol is high potency antipsychotic)
Antipsychotic Drugs Classification, Pharmacology and LongTerm Health

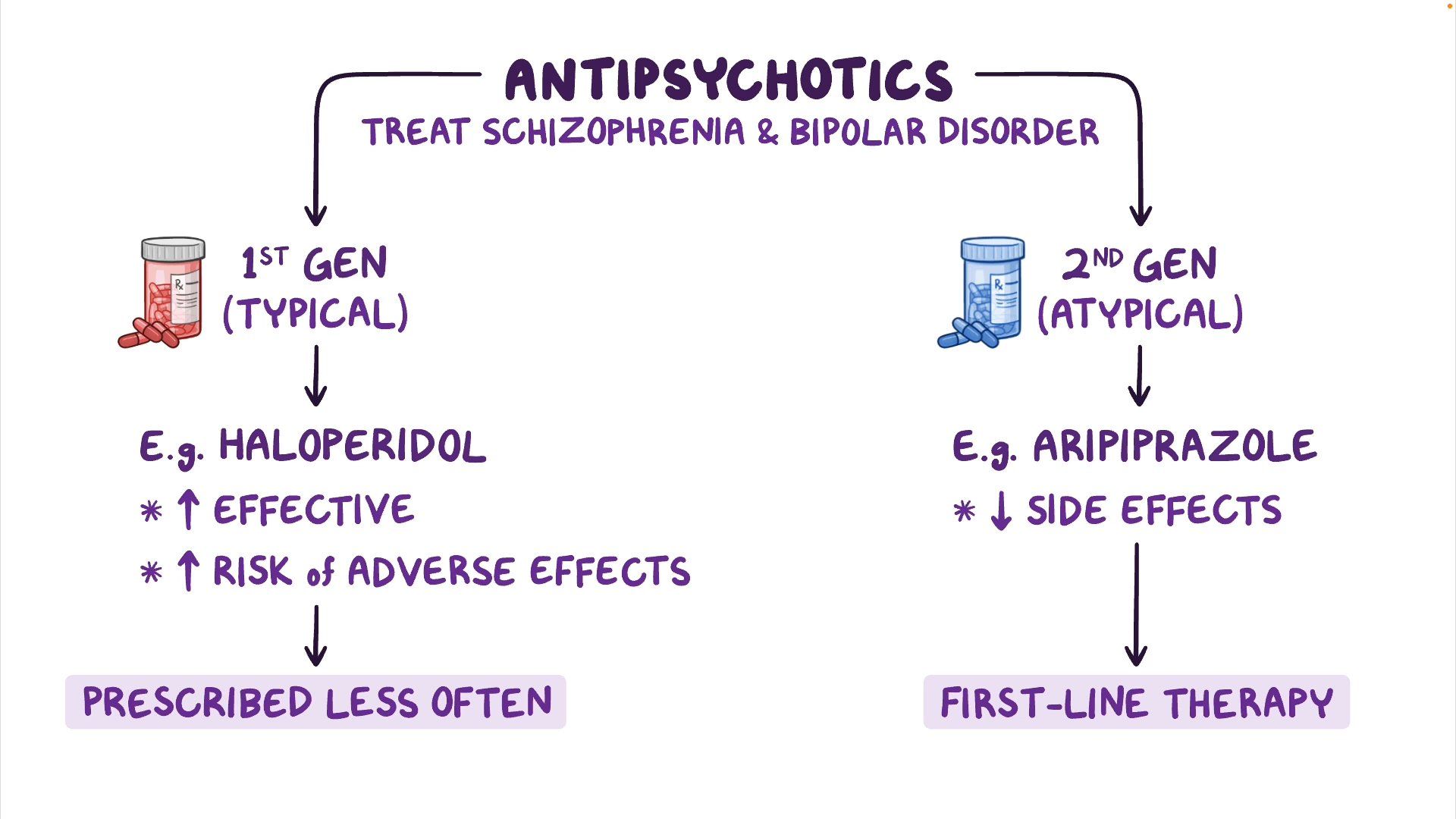
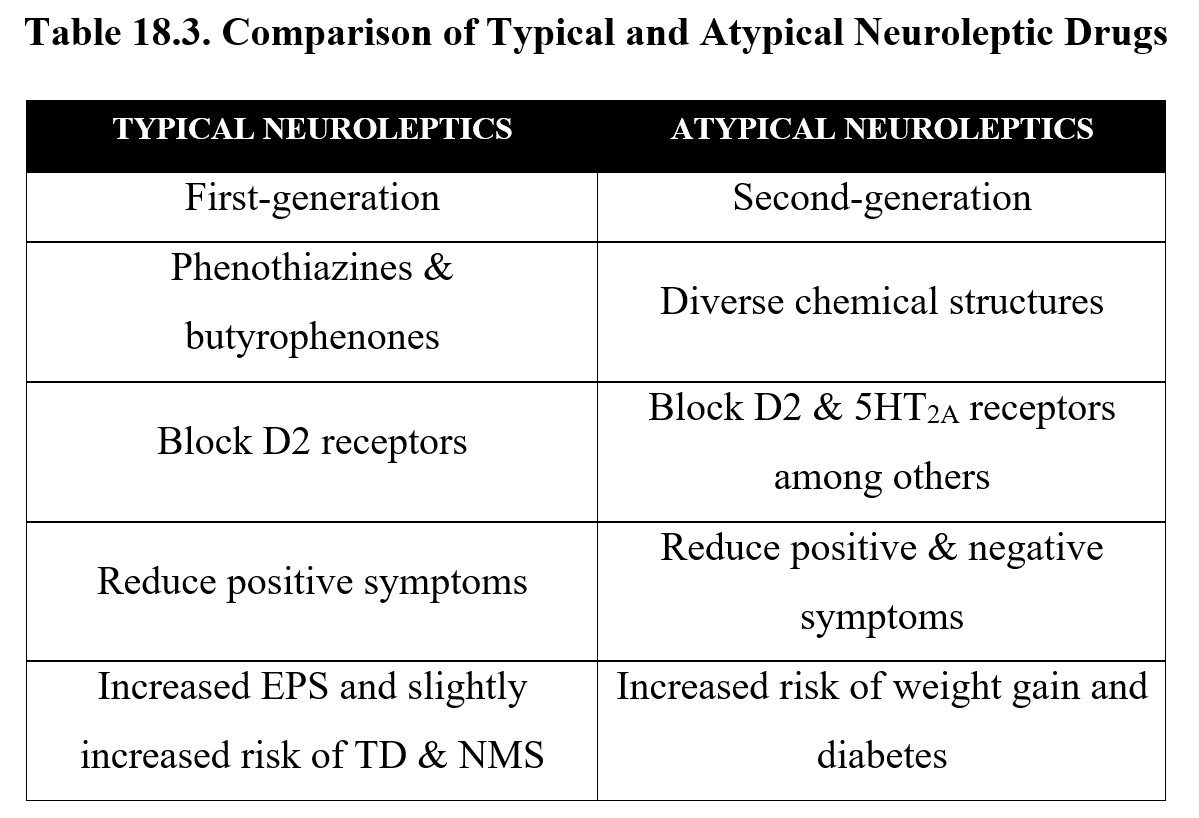
Antipsychotics. First-generation antipsychotics (FGAs) are drugs used primarily for the treatment of schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders. The use of FGAs has declined in the last few years, mainly because of an increase in prescriptions of second-generation agents. Since FGAs are considerably less expensive than newer antipsychotics.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI) Mechanism of Action

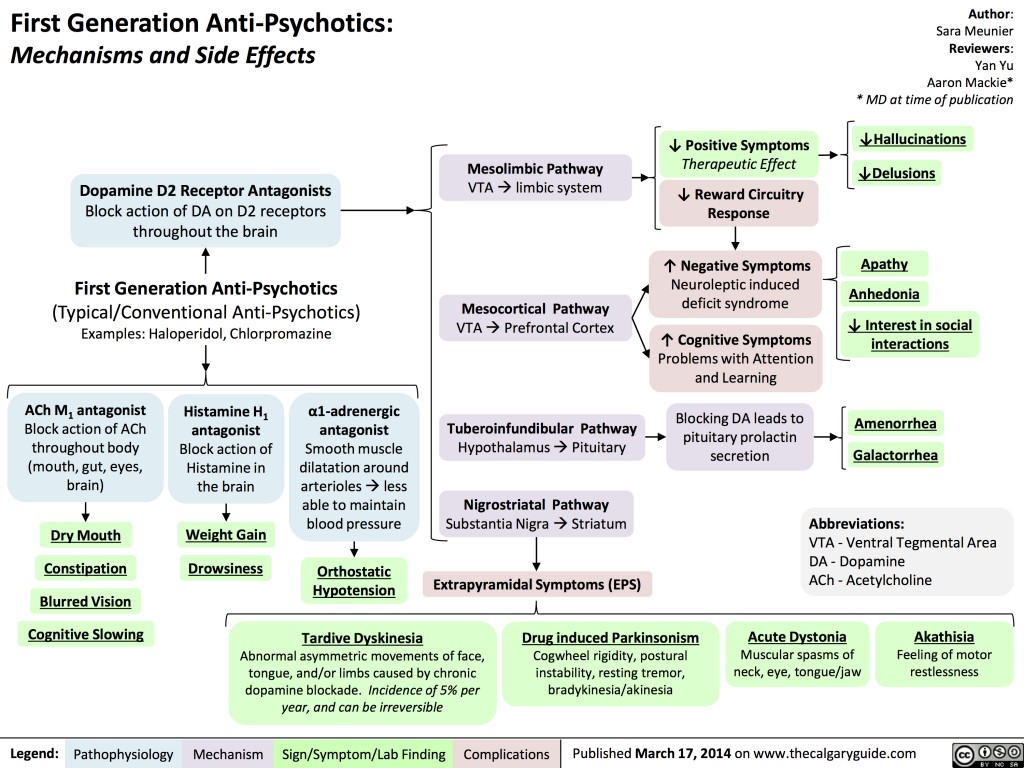
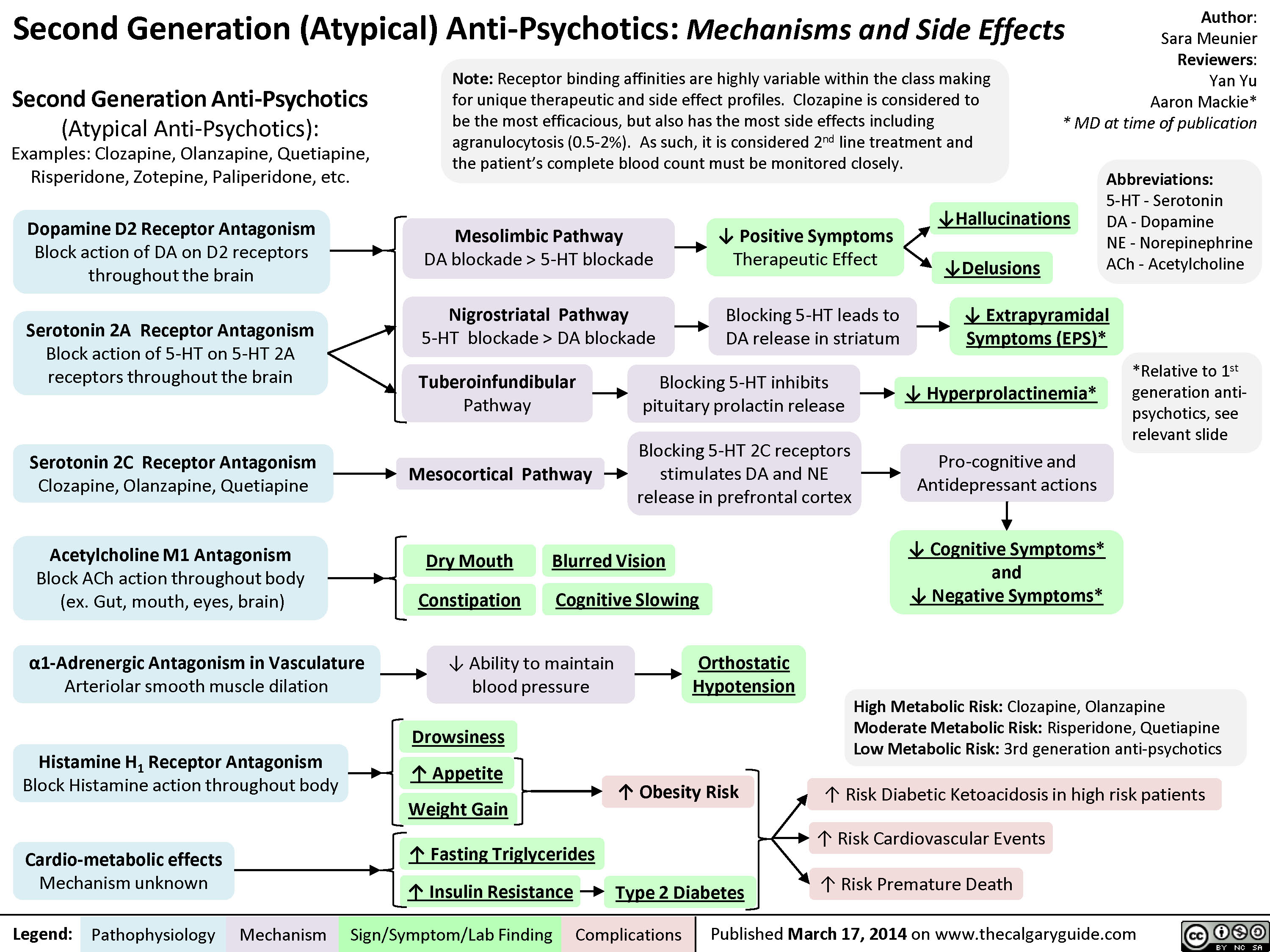
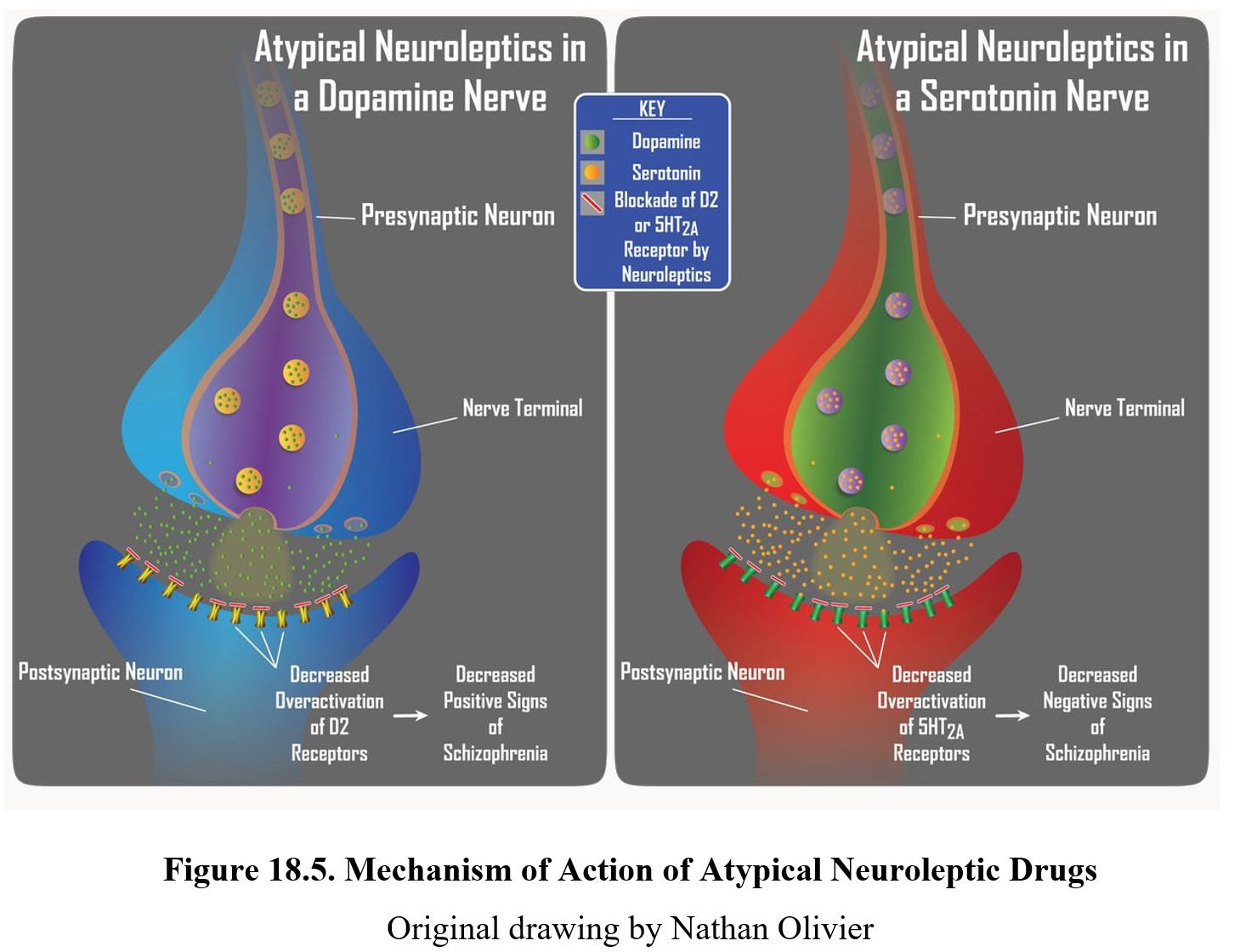
The therapeutic action of an antipsychotic occurs when 65% to 85% of brain dopamine (D2) receptors are occupied. When more than 80% of the dopamine (D2) receptors are occupied, hyperprolactinemia and parkinsonism can result. In addition to percentage occupancy, the duration of time that the antipsychotic drug stays attached to the D2 receptor impacts the degree of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS).
A Simplified Guide to Antipsychotic Medications Mechanisms of Action

In this video , Dr Anshuman has discussed about the MNEMONICS to easily remember the " Classification of ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUGS.
Antipsychotic Drug Therapy Osmosis Video Library
Picmonic. Antipsychotic drugs are typically used to treat positive symptoms of schizophrenia, psychosis, Tourette's syndrome and acute episodes of mania. Typical antipsychotics work by blocking Dopamine D 2 receptors, increasing cAMP. These drugs are highly lipid soluble and are stored in body fat, and are removed very slowly from the body.
Antipsychotic Agents Toxicology HarwoodNuss' Clinical Practice of

Antipsychotics are a heterogeneous group of substances used primarily to treat schizophrenia , psychosis , mania , delusions , and states of agitation . The term neuroleptics was formerly used interchangeably with antipsychotics because early antipsychotic drugs induced apathy
Pharmaceuticals Free FullText Receptors Involved in Mental
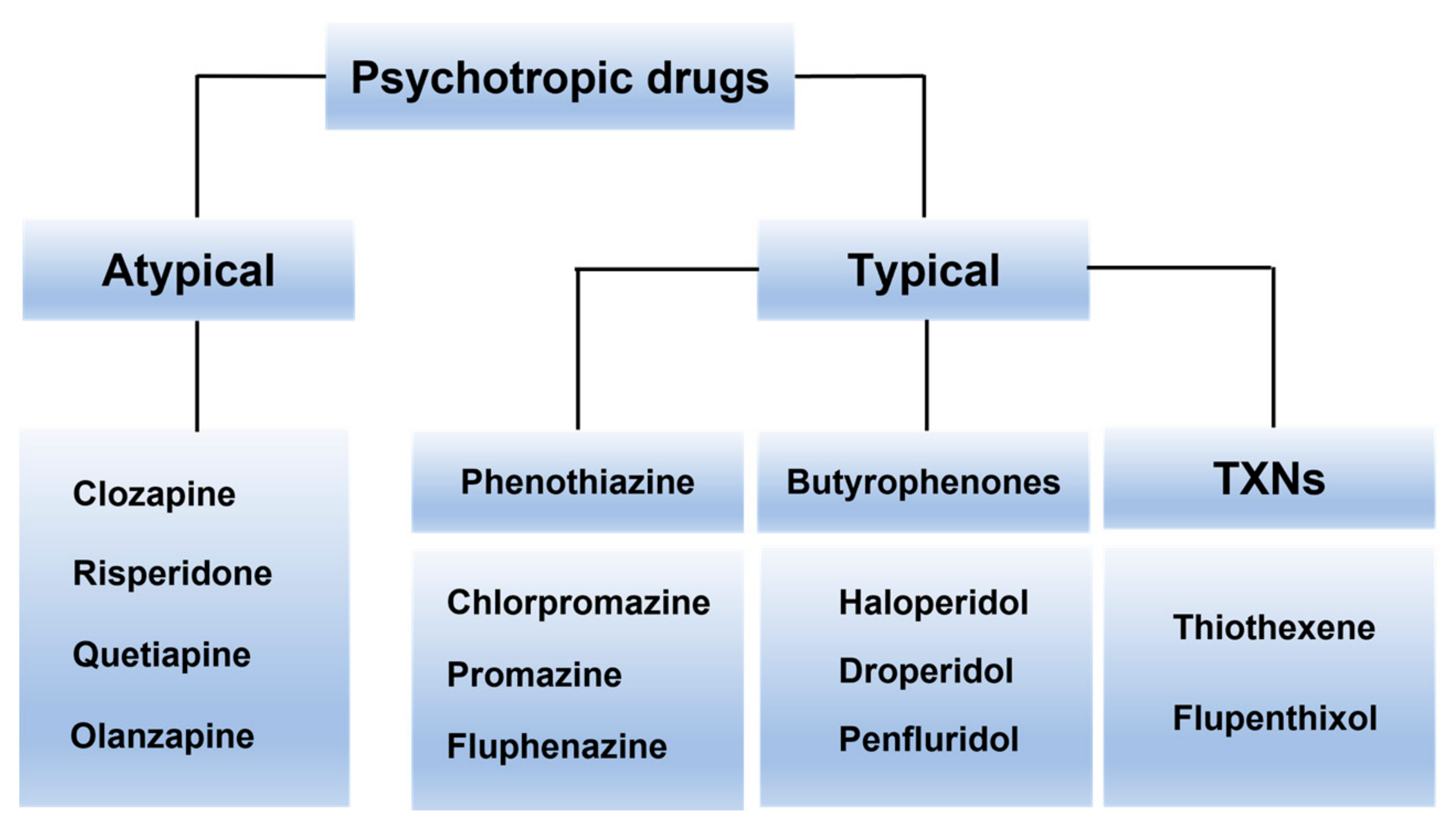
In recent years, the atypical antipsychotics or second-generation antipsychotics have become the drugs of choice for acute psychoses. They are "atypical" as they are differentiated from "conventional" or first-generation antipsychotics based on their clinical profile. This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, safe administration, adverse effects, contraindications.
First Generation AntiPsychotics Mechanisms and Side Effects Calgary
Diazepam 2. Temazepam 3. Lorazepam 4. Clonazepam 5. Alprazolam 6. Chlordiazepoxide
Second Generation Antipsychotics Mechanisms and Side Effects Calgary
Ace Your Pharmacology Classes and Exams with Picmonic: #1 Visual Mnemonic Study Tool for Medicine (MD/DO) Students. With Picmonic, facts become pictures. We've taken what the science shows - image mnemonics work - but we've boosted the effectiveness by building and associating memorable characters, interesting audio stories, and built-in quizzing.
Typical antipsychotics Video, Anatomy & Definition Osmosis

Neuroleptics, also known as antipsychotic medications, are used to treat and manage symptoms of many psychiatric disorders. They fall into two classes: first-generation or "typical" antipsychotics and second-generation or "atypical" antipsychotics. Both first and second-generation antipsychotics are used in various neuropsychiatric conditions. These include attention-deficit hyperactivity.
Chapter 18 Antipsychotics Drugs and Behavior
NIH HHS USA.gov First-generation antipsychotics are dopamine receptor antagonists (DRA) and are known as typical antipsychotics. Second-generation antipsychotics are serotonin-dopamine antagonists and are also known as atypical antipsychotics.
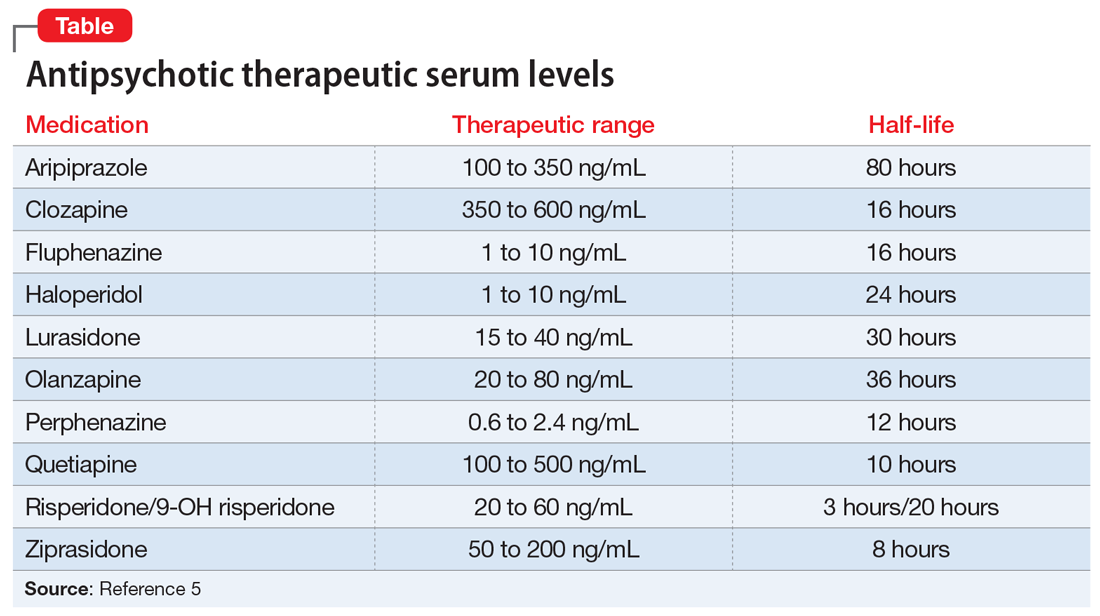
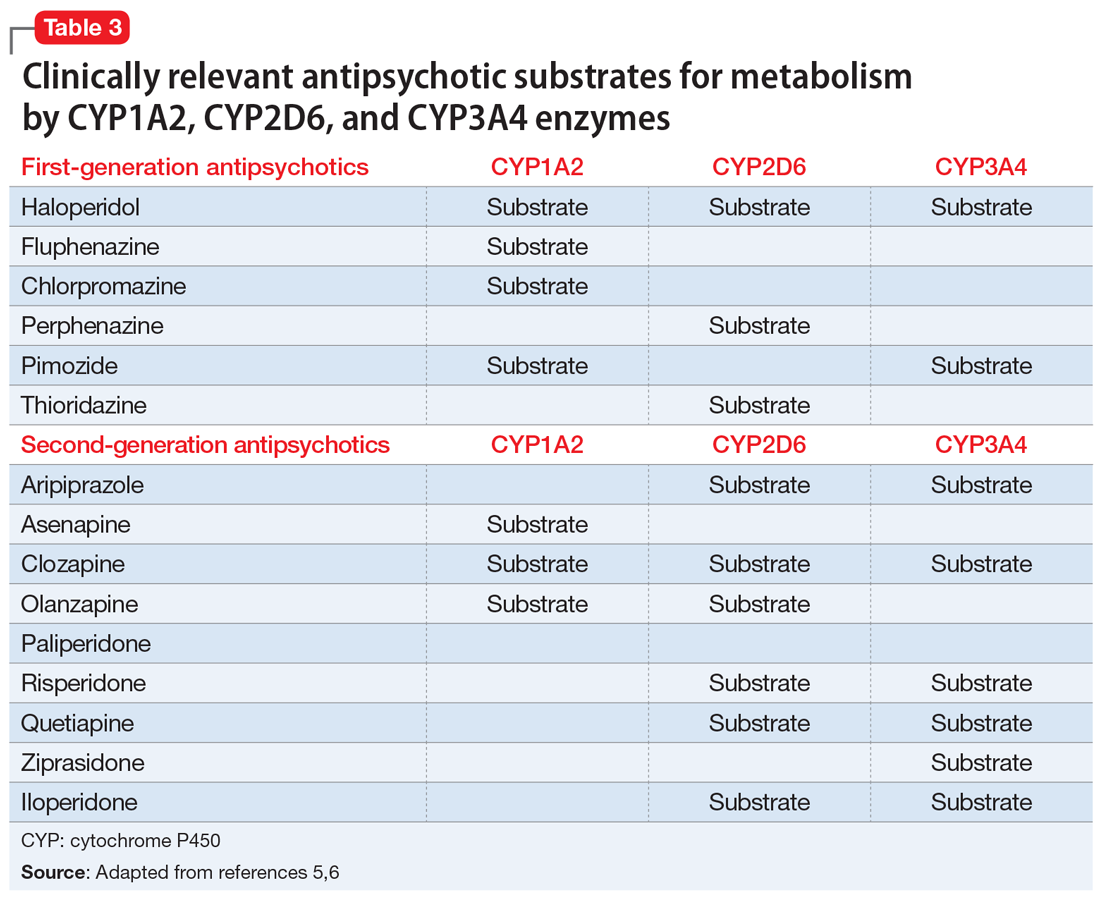
Therapeutic drug monitoring of antipsychotics MDedge Psychiatry
Varenicline or Bupropion And anytime we talk about bupropion, we can't help but think of "that other psych medication that begins with B… Topic: Anxiety medication Mnemonic: What do many people drink when they need to quell some anxiety? B ooze ( pirone ). BUSPIRONE! Recall its indication…used in the treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder.
Antipsychoticinduced priapism Mitigating the risk MDedge Psychiatry
Psychotropic medications are medications that affect the mind, emotions, and behavior. This chapter will review the anatomy and physiology of the central nervous system (CNS) as it relates to mental health disorders and medications and then discuss several classes of psychotropic medications. References 1. DailyMed.
Chapter 18 Antipsychotics Drugs and Behavior
Antipsychotic medication (antipsychotics) are medicines that can help ease the symptoms of a psychosis. Psychosis is a mental health condition that affects how the brain works. There are different types of antipsychotic medications. Sometimes they cause side effects. Talk with your doctor or mental health nurse about what might work best for you.