Hydrogen fuel cells are being dubbed the fuel of the future. So how

Evaluate the feasibility of producing hydrogen from the in-situ combustion of bitumen in a lab-scale apparatus. • At low temperatures, hydrogen production is chiefly governed by coke gasification, while water-gas shift reactions primarily control hydrogen generation at high temperatures. [51] •
Why Hydrogen Hydrogen Advisors
Hydrocarbons. Combustion analysis is a standard method of determining a chemical formula of a substance that contains hydrogen and carbon. First, a sample is weighed and then burned in a furnace in the presence of excess oxygen. All of the carbon is converted to carbon dioxide, and the hydrogen is converted to water in this way.
Tiny engine turns natural gas into hydrogen Everything Linux 101 blog

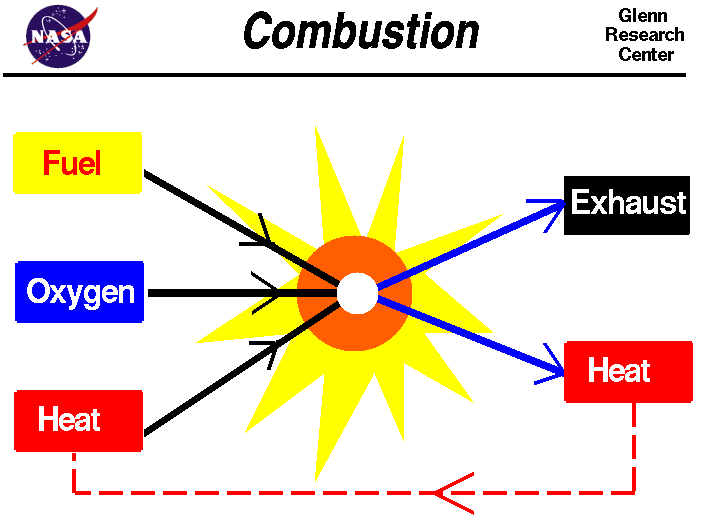
Combustion, or burning, is a chemical process that involves releasing energy from a fuel and air mixture. In the case of hydrogen combustion, liquid or gaseous hydrogen is burned in a modified gas-turbine engine to generate thrust. This process is identical to traditional internal combustion, except hydrogen replaces its fossil fuel counterpart.
Combustion
In the case of a class experiment, where students generate the hydrogen themselves under strict supervision, all the hydrogen generators must be collected once the test tubes have been filled and before any flames are lit, to prevent the possibility of accidental or deliberate ignition of the hydrogen in the generator.
7. Organic Chemistry THOMAS TALLIS SCIENCE
This chapter describes overviews of hydrogen utilization for closed-system internal combustion engines (C-ICE). Basic reactions are explained with a simple H 2 -O 2 combustion system, and hydrogen application to C-ICE is discussed in comparison to other conventional fuels, also followed by case studies of hydrogen combustion systems.
PPT Equations & Reactions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID

The new kinetic mechanism for hydrogen combustion which includes updated kinetics and new transport properties was found in good agreement with the consistent dataset of the burning velocity measurements for hydrogen flames obtained using the heat flux method at atmospheric pressure for which the behavior of the previous model of the author was.
1.5 million pound awarded to hydrogen combustion project

publications further addressing two of the most important reactions involving the hydrogen radical, i.e., the branching reaction [16], H + O2 = OH + O (R1), and the competitive reaction [17-20], H + O2 (+M) = HO2 (+M) (R2). While some of the results presented in [19] were known at the time of our earlier
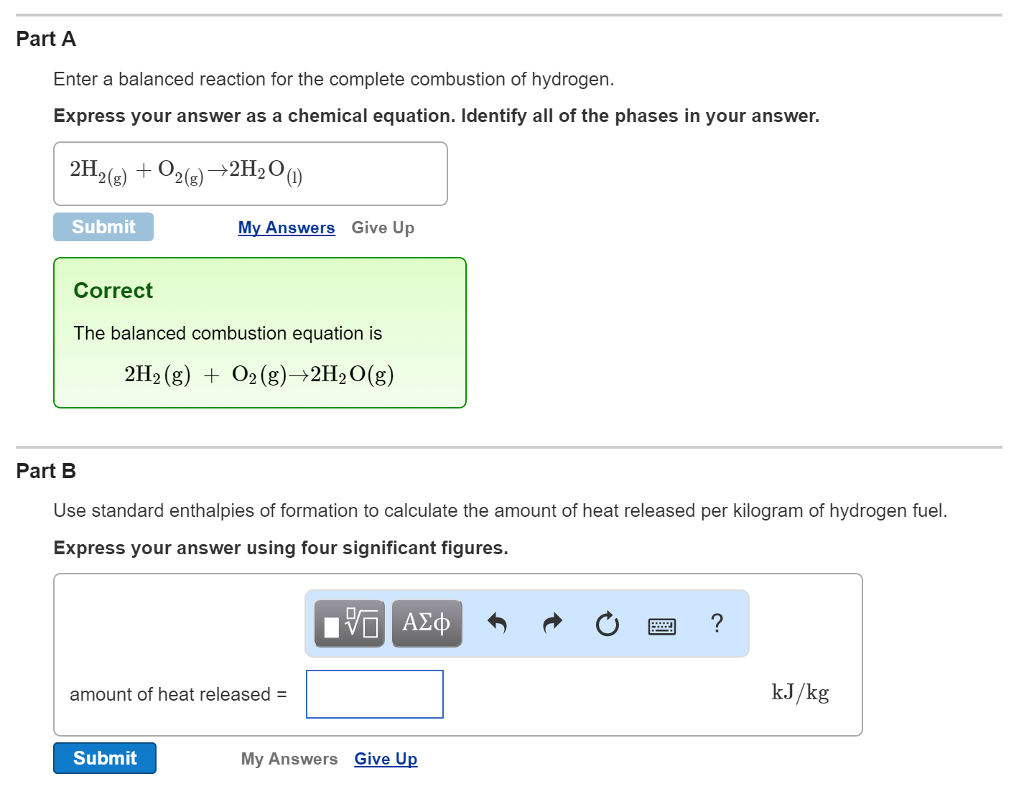
Solved Enter a balanced reaction for the complete combustion
The chemical reaction looks like this: CH4 + H2O (+ heat) → CO + 3H2 In the second step, carbon monoxide combines with water. The products are carbon dioxide (CO 2) and more hydrogen gas. The chemical reaction looks like this:
Instant Hydrogen Production For Powering Fuel Cells FuelCellsWorks

Reaction Kinetics of Hydrogen Combustion 69 Fig. 3 Calculated ignition delay times (IDTs) of a stoichiometric hydrogen-air mixture at 800 K initial temperature as a function of pressure using homogeneous, isochoric, adiabatic simulations. The dashed line shows the IDTs ina large vessel (without walleffects) and the solid line shows the
Combustion of hydrogen releases 142 j/g of hydrogen reacted. How many

If the temperature is high enough a long pair of oxygen could break the (the lone pair will be donated to the bond) bond and form (each H gets one electron because of their equal electronegativity). is very unstable and one will immediately react with the empty oxygen orbital, the other will break the bond.
Free Online Help When hydrogen sulfide gas , H2S react with oxygen
All qualitative features of the hydrogen combustion system can be explained by a 10-step mechanism. Several web sites are recommended here which contain comprehensive collections of recent hydrogen combustion mechanisms, direct and indirect experimental data, and theoretical determinations. Keywords Hydrogen combustion Inverted S-curve
Testing of hydrogen fuelled internal combustion engine underway by

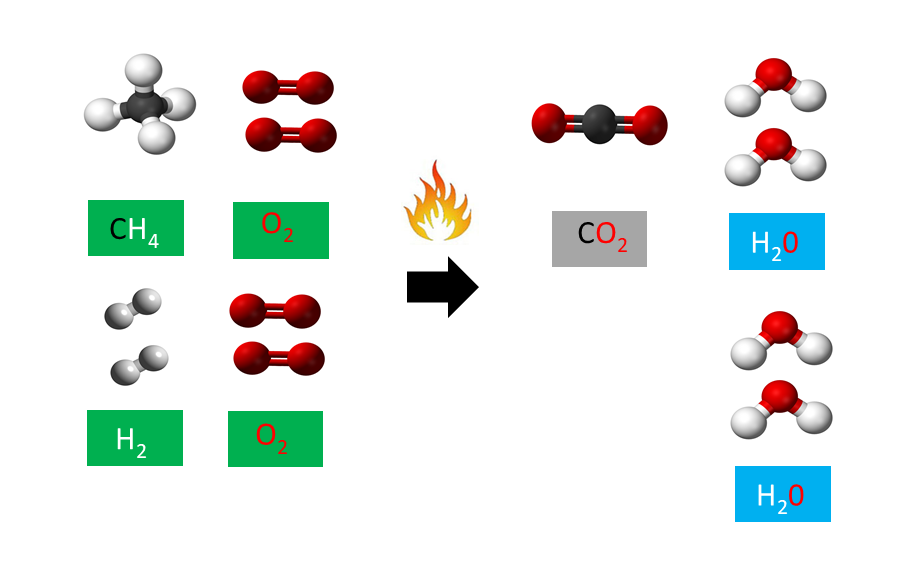
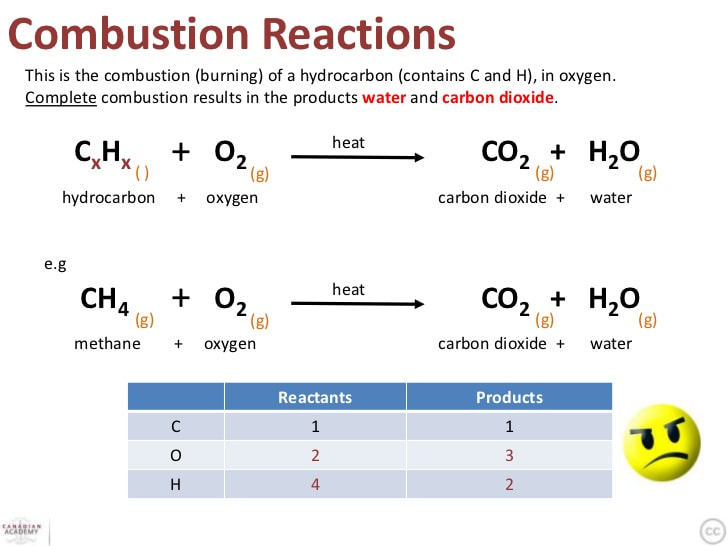
Combustion Reactions. A combustion reaction is a reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen gas, releasing energy in the form of light and heat. Combustion reactions must involve \(\ce{O_2}\) as one reactant. The combustion of hydrogen gas produces water vapor (see figure below).
The initial stage of combustion. a Main reaction pathways in the

As hydrogen combustion occurs in an atmosphere containing nitrogen and oxygen, however, it can produce oxides of nitrogen known as NOx. In this way, the combustion process is much like other high temperature combustion fuels, such as kerosene, gasoline, diesel or natural gas. Therefore, hydrogen combustion engines are not considered zero emission.
Combustion reaction chains of hydrogen and methane Download
Hydrogen combustion is the process by which hydrogen reacts with an oxidizing agent and burns. Hydrogen combustion is an exothermic combustion, meaning that it releases heat energy. Endothermic processes, on the other hand, absorb energy. Hydrogen burns based on the chemical formula 2H 2 + O 2 → 2H 2 O, meaning that it reacts with oxygen.
Hydrogen Storage
Hydrogen energy, with the advantages of being pollution-free and having high combustion efficiency and a high utilization rate, has been widely developed as a substitute for traditional fossil fuels. The hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) plays an important role in water electrolysis. Metal-free electrocataly
Hydrogen The Burning Question Features The Chemical Engineer

Hydrogen Combustion: Features and Barriers to Its Exploitation in the Energy Transition by Eugenio Giacomazzi *,†,‡, Guido Troiani ‡, Antonio Di Nardo ‡, Giorgio Calchetti ‡, Donato Cecere ‡, Giuseppe Messina ‡ and Simone Carpenella ‡