Annual WelltoWheel Emissions By State Shows Growing Strength Of EV Usage

Introduction Since the latter part of the 20th century, climate change has become a global issue. Governments and people around the world noticed the negative effects that excessive greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions can have on our nature and society.
figure 04.3 ok.eps
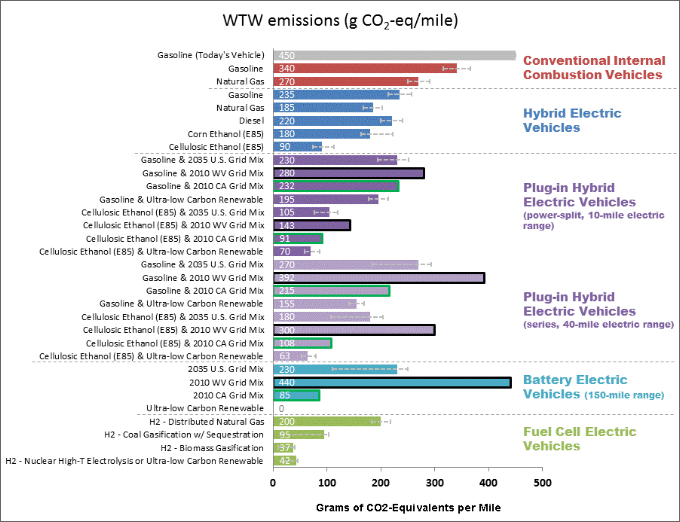
Well-to-wheel emissions include all emissions related to fuel production, processing, distribution, and use. In the case of gasoline, emissions are produced while extracting petroleum from the earth, refining it, distributing the fuel to stations, and burning it in vehicles.
New Generation Transport don't be taken for a ride Page 4

The height of the stacked column shows instead total well-to-wheel emissions of fuel cell electric vehicles considering current and projected share of hydrogen production pathways. Therefore, the difference between the red column and the total indicates the theoretical well-to-wheel greenhouse gas emissions reduction potential of FCEVs. The.
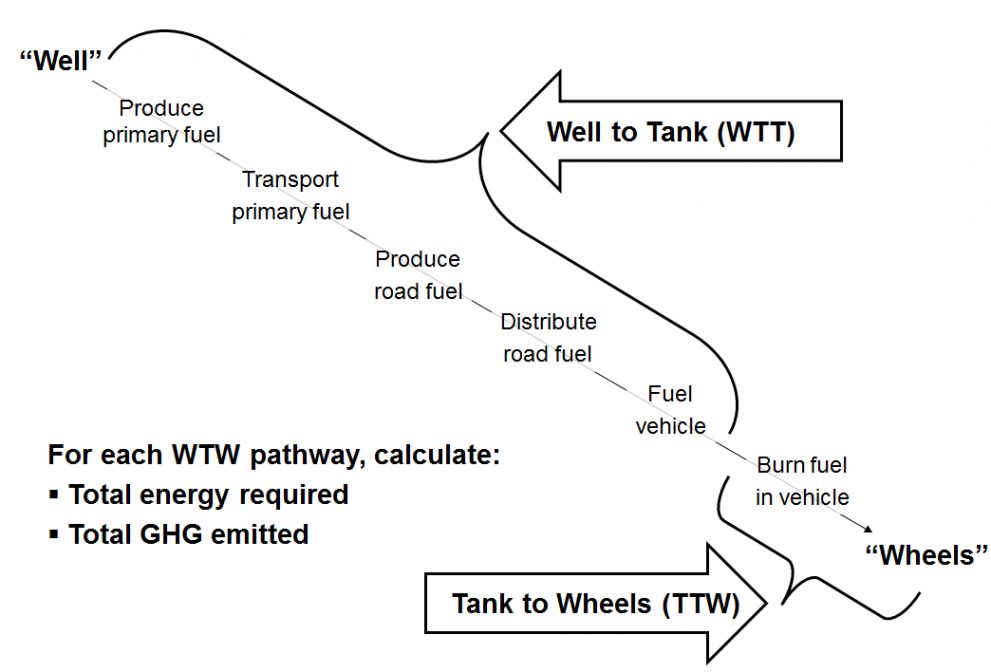
Well to Wheel Emissions Simplified

These analyses are known as well to wheel studies. From these analyses, EVs have been shown to reduce energy consumption by up to 50% and GHG emissions by up to 60%. Carbon Emissions (g CO2/km) 300.0 250.0 200.0 150.0 100.0 50.0 0.0 2006 ICE 2030 ICE Diesel HEV PHEV-30 FCV BEV
Ask an Expert Taking a Life Cycle Approach to Automotive Environmental

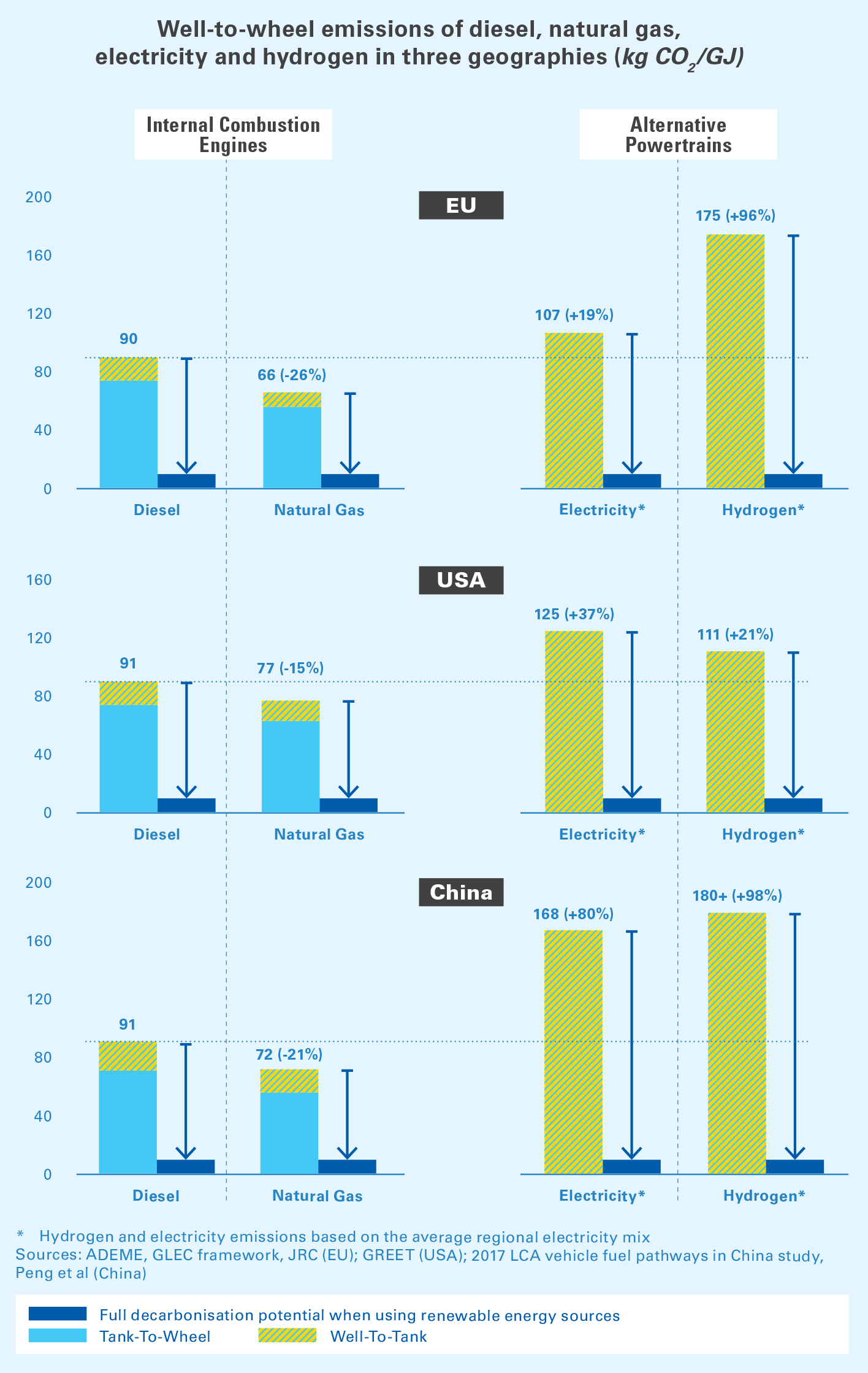
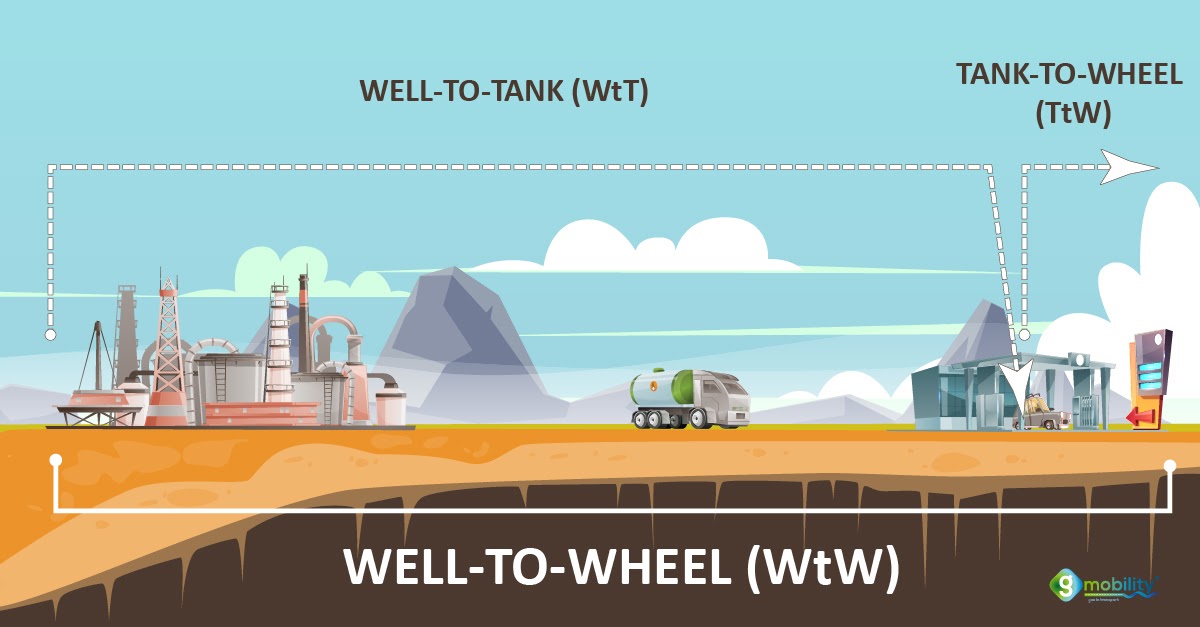
Well-to-wheels (WtW) is used to assess the LCA of fuels, including all phases of its life cycle - from the extraction of raw materials to their use. There are two components to the well-to-wheels assessment: well-to-tank (WtT) and tank-to-wheels (TtW). WtT includes the fuel production phases, and TtW the use of fuel.
Images of WelltoWheel JapaneseClass.jp

This paper assesses the well-to-wheel (WTW) greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of energy carriers for heavy-duty vehicles, analyzing the effect of the carbon intensity of the electricity used in production. The results show that energy carriers with high electricity dependence are not necessarily better than diesel from a WTW perspective.
Well to wheels analysis of potential reduction in greenhouse gas

Integrating well-to-wheel greenhouse gas emissions . Comparing the greenhouse gas emissions impacts of vehicles across different fuel-powertrain options requires looking beyond their rated tailpipe CO 2 emissions. A coherent and complete comparison requires analysing the emissions incurred across the entire life cycle, and includes both the "fuel-cycle" or "well-to-wheel" emissions.
‘Welltowheel’ greenhouse gas emissions of oil sands pathways. Notes

The well-to-wheels analyses by JEC pursue the objectives of estimating: greenhouse gas emissions, energy efficiency and industrial costs of a wide range of automotive fuels and power-trains options significant for Europe in 2020 and beyond. © EU, 2016 The outcome serves as a sound and broadly accepted scientific reference.
Fact 686 August 1, 2011 Emissions and Energy Use Model GREET
Well-to-Wheels Energy and Emission Impacts of Vehicle/Fuel Systems Development and Applications of the GREET Model Michael Wang Center for Transportation Research Argonne National Laboratory California Air Resources Board Sacramento, CA, April 14, 2003 Vehicle and Fuel Cycles: Petroleum-Based Fuels Vehicle Cycle Fuel Cycle Well to Pump
WelltoWheels Analyses
Well-to-Wheels Analysis of Advanced Fuel/Vehicle Systems — A North American Study of Energy Use, Greenhouse Gas Emissions, and Criteria Pollutant Emissions
Well to Wheel Emissions Simplified

JEC Well-To-Wheels report v5 Published 28 Mar 2022 1 min read JRC (the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission), EUCAR and Concawe have updated their joint evaluation of the Well-to-Wheels energy use and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions for a wide range of potential future fuel and powertrain options, first published in December 2003.
Welltowheel GEEWTW_ICEB emissions (gCO2eq /km) by bus type

Highlights • EVs are going to dominate vehicle sales and later form a major portion of the fleet. • BEVs outperform other types of EVs under current electricity mix in both countries. • Hydrogen produced by water-electrolysis produces least emissions. • FCEVs will play a critical role in emission reduction in the long run. •
Flawed CO₂ emissions policy jeopardises commercial transport
Well to wheel analysis is a comprehensive method for assessing energy efficiency and emissions. It takes into account the total energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions throughout the entire life cycle of an energy source. Well-to-wheel vs tank-to-wheel emissions
Well to Wheel Emissions Simplified

Well-to-wheel emissions include those from fuel production and vehicle use, but not vehicle manufacturing. Positive emissions are from the global EV fleet (BEVs and PHEVs). Negative emissions are those that would have been emitted by an equivalent ICE vehicle fleet. The red dots denote net GHG emissions savings from EVs in comparison with an.
Selecting Specification of Electric Vehicle 2654 Words Coursework
Well-to-wheels greenhouse gas emissions for cars by powertrains - Charts - Data & Statistics - IEA Well-to-wheels greenhouse gas emissions for cars by powertrains Last updated 25 Feb 2021 Download chart Cite Share gCO2-eq/km ICE HEV PHEV BEV FCEV 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 IEA. Licence: CC BY 4.0 Range World average Notes
Micromobility, Light and HeavyDuty What’s the Electrification Score?

The well-to-wheel (WTW) methodology is a useful tool for comparing energy carriers for transport. However, for the comparison to be valid, it requires that the differences in parts excluded from the system boundary are not too great.. Well-to-wheel greenhouse gas emissions of heavy-duty transports - influence of electricity carbon intensity.