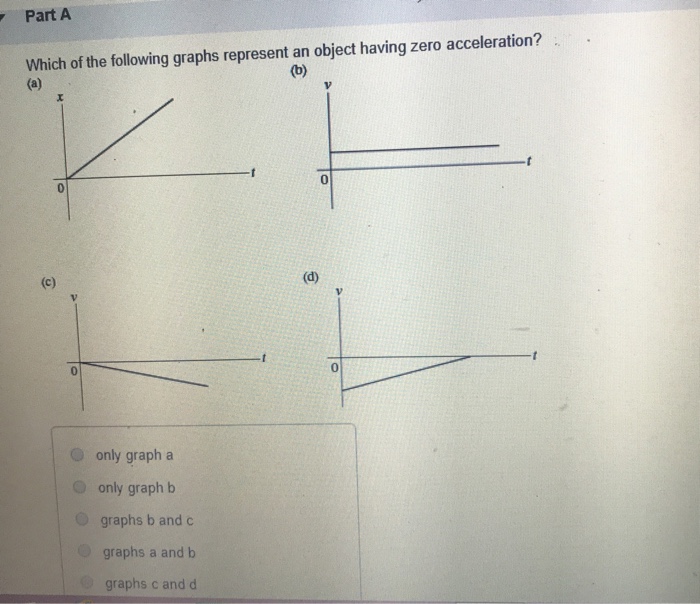
Solved Part A Which of the following graphs represent an
Newton's second law describes the affect of net force and mass upon the acceleration of an object. Often expressed as the equation a = Fnet/m (or rearranged to Fnet=m*a), the equation is probably the most important equation in all of Mechanics. It is used to predict how an object will accelerated (magnitude and direction) in the presence of an unbalanced force.
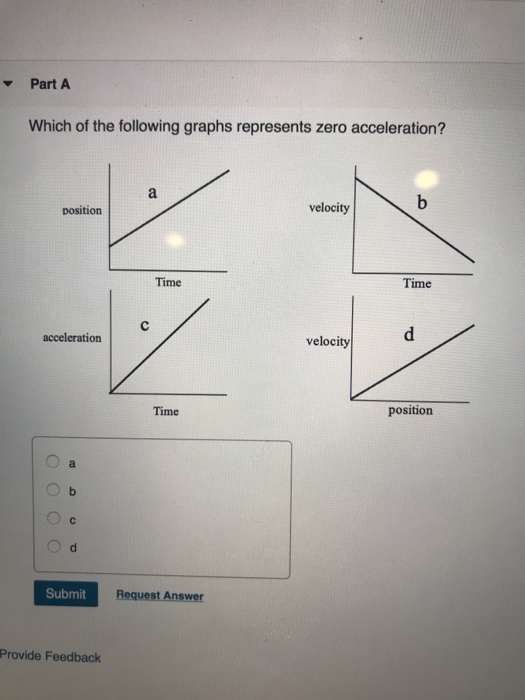
Solved Part A Which of the following graphs represents zero
In Figure 3.4.5 3.4. 5, instantaneous acceleration at time t 0 is the slope of the tangent line to the velocity-versus-time graph at time t 0. We see that average acceleration a¯ = Δv Δt a ¯ = Δ v Δ t approaches instantaneous acceleration as Δt approaches zero.
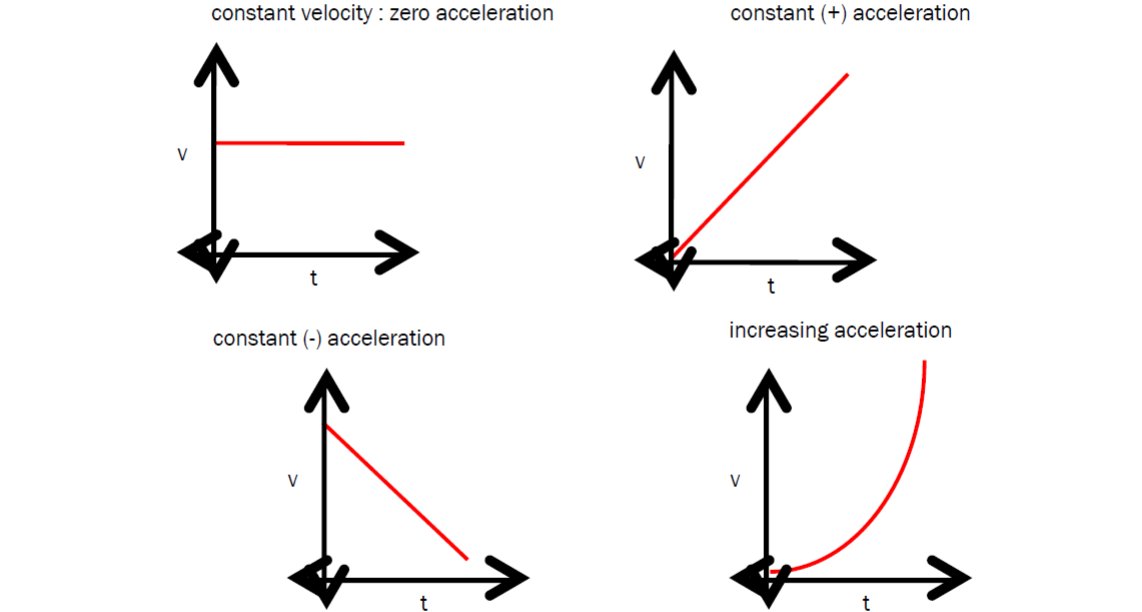
Acceleration Graph from Notes Acceleration graph ShowMe
Finding the velocity Let's start by looking at the object's initial velocity, and confirm that it must be zero. When an object starts from rest (at x (0)=0 x(0) = 0) and starts to accelerate at the rate \gamma γ, its position a time \Delta T ΔT later is x (\Delta T) = \frac12\gamma\left (\Delta T\right)^2. x(ΔT) = 21γ (ΔT)2.
NCERT Q9 State which of the following situations are possible and

So the forces acting on the object can cancel each other out and the object would have 0 acceleration. Using the example of hanging cheese, the vertical forces cancel each other out, as sin60 times 23 is approximately equal to 20, so the net force would end up zero, but there are still these forces acting on it.
Draw the position time graph for stationary body +ve velocity ve

Definition: Average Acceleration. The average acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes, ˉa = Δv Δt = vf − v0 tf − t0. where ˉa is average acceleration, v is velocity, and t is time. (The bar over the a means average .) Because acceleration is velocity in m/s divided by time in s, the SI units for acceleration are m / s2.
Lord Jessica's Physics Blog of Doom Distance, Velocity, Acceleration
1. v = v 0 + a t 2. Δ x = ( v + v 0 2) t 3. Δ x = v 0 t + 1 2 a t 2 4. v 2 = v 0 2 + 2 a Δ x Since the kinematic formulas are only accurate if the acceleration is constant during the time interval considered, we have to be careful to not use them when the acceleration is changing.
In a linear S.H.M., the acceleration of the particle is zero, when its

Q 3. If the net unbalanced external force acting on an object is zero, then the. (A) Velocity of the object may or may not be zero. (B) Acceleration of the object must be zero. (C) Velocity of the object must be non-zero. (D) Acceleration of the object must be a non-zero constant. Choose the correct option:
Thread by Doc_MD18 "NMAT Review Must Know Physics [Thread] (Topics
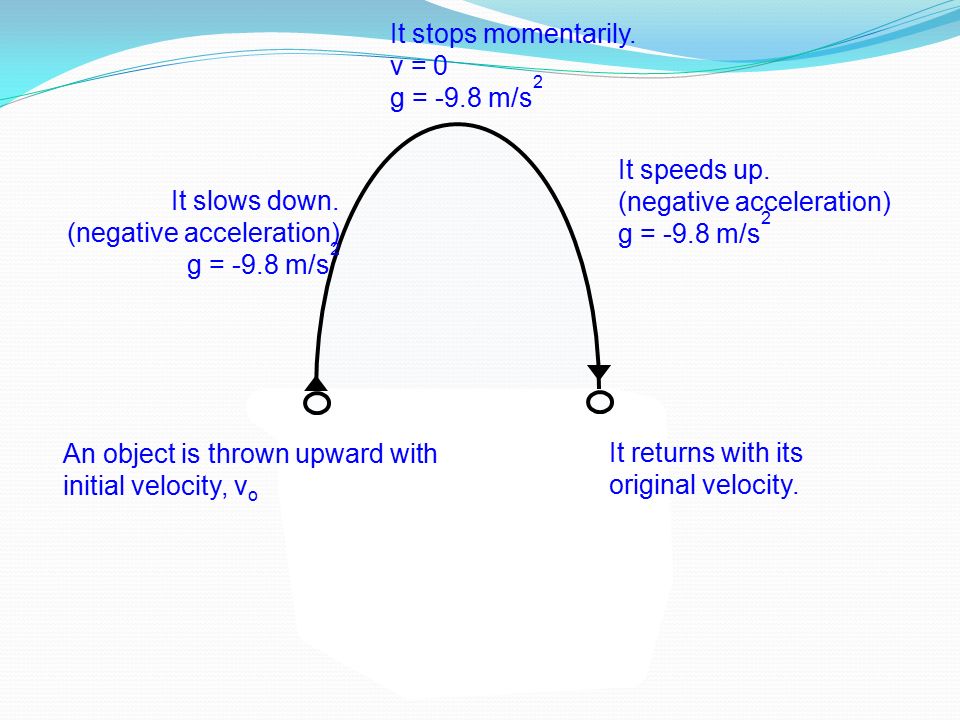
The acceleration function is linear in time so the integration involves simple polynomials. In Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\), we see that if we extend the solution beyond the point when the velocity is zero, the velocity becomes negative and the boat reverses direction.
[Physics] The instant an accelerating object has zero speed, is it

5 Answers Sorted by: 18 The confusion comes from how you have written the equation. If you write it like this Fnet = ma F n e t = m a it will be easier to see your error. You are exerting a force on the boulder, but net force is zero. This means that other forces such as friction are canceling your force out. In this case.
PPT Physical Science CHS 201314 PowerPoint Presentation, free
In contrast, instantaneous acceleration is measured over a "short" time interval. The word short in this context means infinitely small or infinitesimal — having no duration or extent whatsoever. It's a mathematical ideal that can only be realized as a limit. The limit of a rate as the denominator approaches zero is called a derivative.Instantaneous acceleration is then the limit of average.
Find the acceleration of an object when the velocity is zero YouTube

The above equation says that the acceleration, a , is equal to the difference between the initial and final velocities, v f − v i , divided by the time, Δ t , it took for the velocity to change from v i to v f . [Really?] Note that the units for acceleration are m / s s , which can also be written as m s 2 .
When is it possible for velocity to be zero for an object that would be
Key terms Equations Newton's second law of motion Newton's second law says that the acceleration and net external force are directly proportional, and there is an inversely proportional relationship between acceleration and mass.
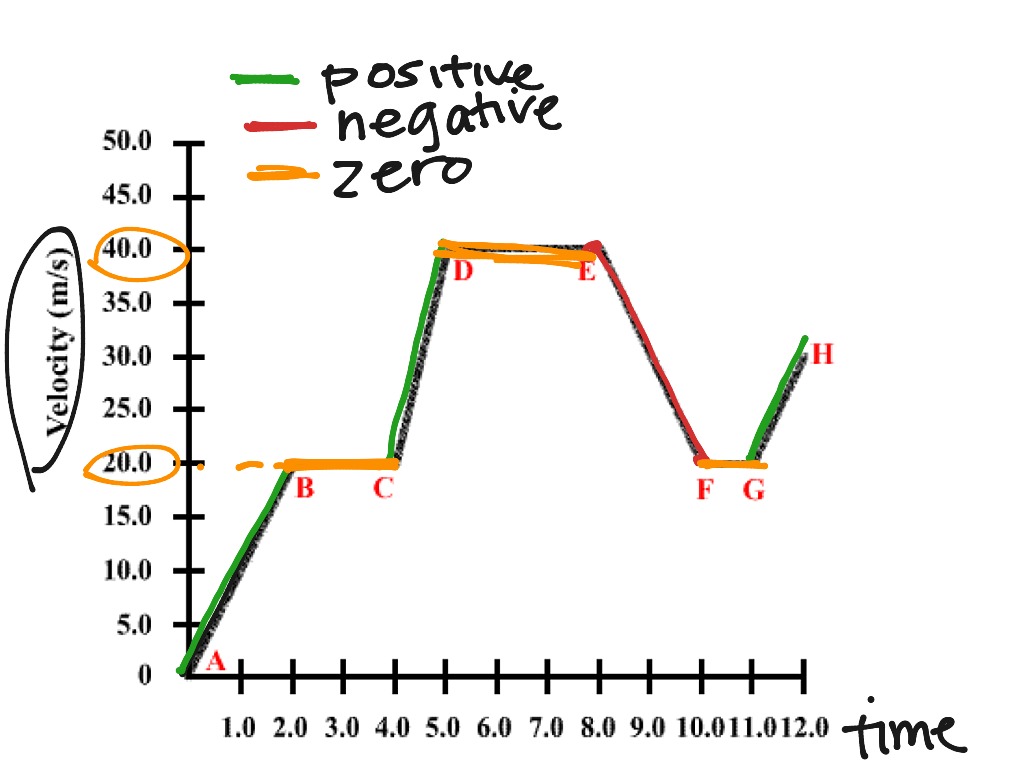
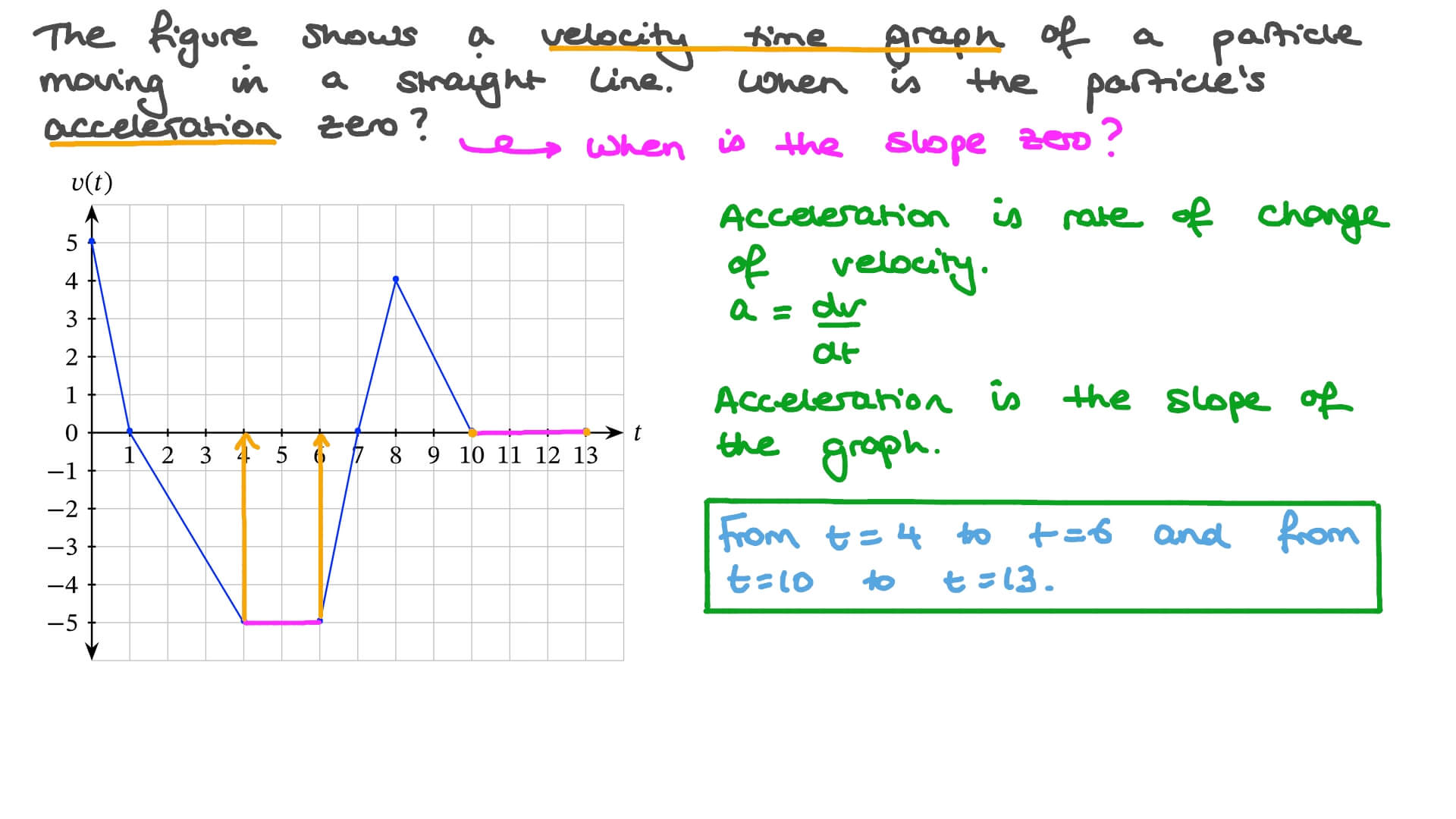
Question Video Finding the Time Intervals in Which the Acceleration of
by Jidan / April 25, 2023 Hey, Physics Thinker In this tutorial we will discuss an important concept which is Zero Acceleration. You need to understand what effect a particle has on its motion when it moves at zero acceleration. Table of Contents What is Zero Acceleration? Impact on Motion Impact on Velocity Impact on Force Questions and Answers
Can you have a zero acceleration but nonzero velocity? Explain with

Figure 3.8 When acceleration is constant, the slope of 2d versus t2 gives the acceleration. The fifth kinematic equation relates velocity, acceleration, and displacement. v2 = v20 + 2a(d − d0). v 2 = v 0 2 + 2 a ( d − d 0). 3.8. This equation is useful for when we do not know, or do not need to know, the time.
Question Video Determining When Acceleration Is Zero Based on Time and

Notation First, let us make some simplifications in notation. Taking the initial time to be zero, as if time is measured with a stopwatch, is a great simplification. Since elapsed time is Δ t = t f − t 0, taking t 0 = 0 means that Δ t = t f, the final time on the stopwatch.
Why isn't acceleration always zero whenever velocity is zero, such as

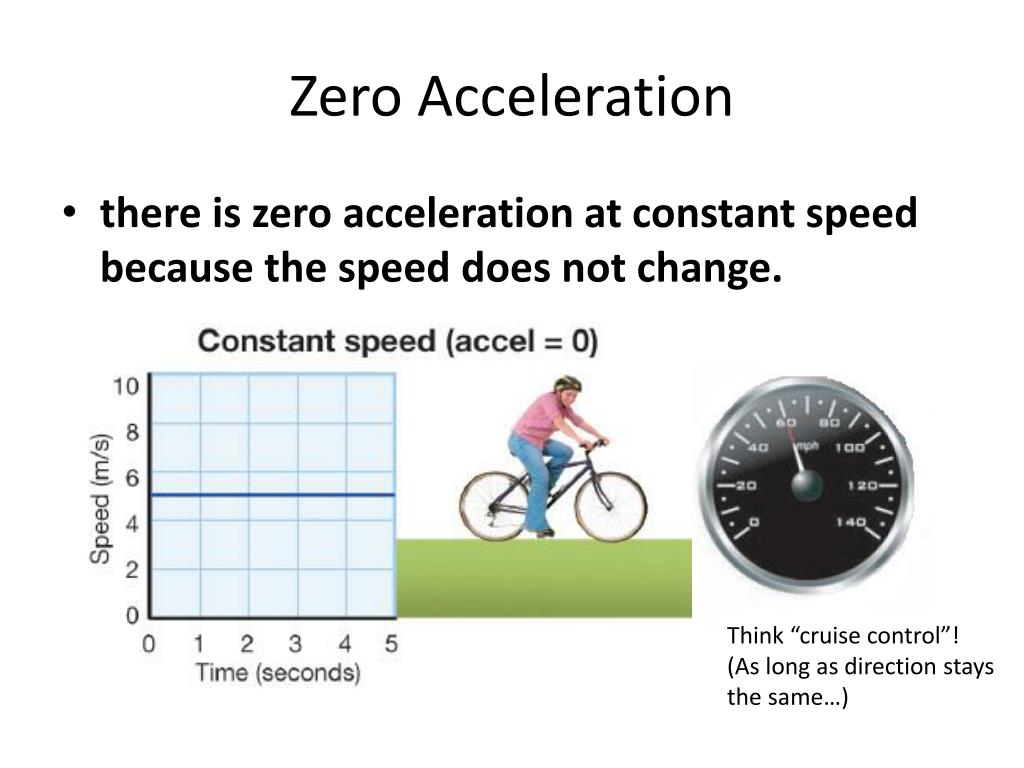
The acceleration of the car is zero, and in this case, the velocity is also zero. When your car is moving at constant velocity down the street, the net force must also be zero according to Newton's first law. The car's frictional force between the road and tires opposes the drag force on the car with the same magnitude, producing a net.